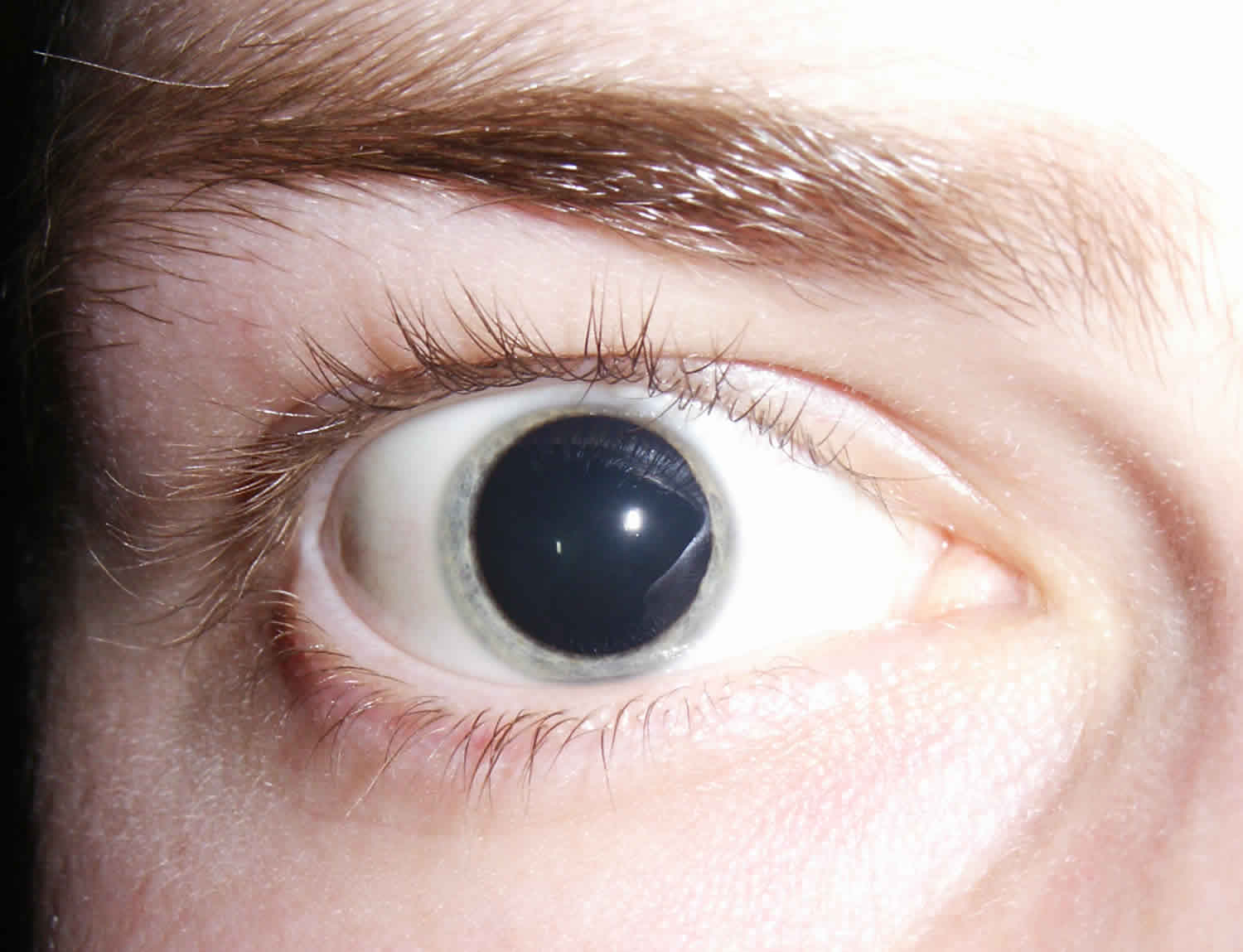
Could a simple change in pupil size reveal a hidden danger within your eye or brain? Understanding the nuances of mydriasis, or dilated pupils, is crucial, as it can be a window into various health conditions, from benign responses to serious neurological events.
Mydriasis, the term for pupils larger than usual, is a fascinating phenomenon. It isn't always a cause for alarm. In fact, our pupils naturally dilate in response to dim lighting, allowing more light to enter the eye for better vision. They also expand when we focus on distant objects, a natural adjustment to our visual environment. Moreover, the use of dilating eye drops, a standard procedure during eye exams, intentionally widens the pupils to provide a clearer view of the eye's internal structures.
However, mydriasis can also signal underlying health concerns. Medications, recreational drugs, and even certain injuries can trigger this dilation. In some individuals, mydriasis poses a risk factor for angle-closure glaucoma, a serious eye condition where the angle between the iris and cornea narrows, potentially leading to a sudden increase in eye pressure. This is particularly concerning in those with "narrow angles," a pre-existing anatomical condition. Conversely, the opposite of mydriasis, pinpoint pupils (miosis), can also be indicative of specific conditions or substance use.
Read also:Movierulz Updates Latest News Reviews Downloads Stay Informed
In the realm of neurology, the significance of pupil size takes on a different dimension. The pressure that builds inside the brain after a head injury, stroke, or tumor can damage the iris muscles, leading to dilated pupils. This can be especially concerning if one pupil is fixed and dilated, particularly in an unconscious patient. In such cases, it can raise suspicion of a brain herniation due to an intracranial mass lesion. A fixed dilated pupil in an awake patient, however, does not typically suggest herniation.
The following table provides a comprehensive overview of Mydriasis and its associated factors. It is designed for easy integration into various platforms, including WordPress:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Pupil dilation beyond a diameter of 5 mm; the opposite of miosis. |
| Causes (Normal) | Dim light, focusing on distant objects, dilating eye drops. |
| Causes (Medical/Other) | Medications, recreational drugs, head injuries, strokes, tumors (affecting iris muscles). |
| Association with Eye Conditions | Risk factor for angle-closure glaucoma in individuals with narrow angles. |
| Neurological Significance | Fixed dilated pupil in unconscious patients can indicate herniation due to intracranial mass. |
| Traumatic Mydriasis | Can result from ocular injuries (e.g., sweetgum ball) leading to accommodative dysfunction. |
| Pharmacologic Mydriasis | Caused by certain topical agents; testing involves assessing pupil response. |
| Other Ocular Disorders | Various conditions can prevent pupil constriction, affecting its normal function. |
| Related Terms | Dilated pupil, enlarged pupil. |
| Relevance | Mydriasis can happen for many reasons, such as a normal response to light, medication or drug use, eye exams, and medical conditions. |
For additional in-depth information, consult the National Eye Institute website, a trusted source for eye health information: National Eye Institute
The case of traumatic mydriasis and accommodative dysfunction stemming from a sweetgum ball ocular injury highlights the potential for long-term visual complications. In this specific scenario, the injury, which occurred eight years prior, resulted in these visual disturbances. The precise details of the injury and the individual's subsequent visual history underscore the importance of a thorough examination.
The underlying mechanism of pharmacologic mydriasis, caused by topical agents, and how this mydriasis is identified and confirmed also warrants careful consideration. To differentiate pharmacologic mydriasis from other causes, doctors must assess the pupil's response to certain light or other stimuli.
When a patient presents with mydriasis, a detailed medical history, including any medications or drug use, is vital. A careful neurological examination is also important. Imaging studies, such as a CT scan or MRI, may be necessary to assess the brain and rule out any underlying structural causes, such as a brain tumor or aneurysm. This comprehensive evaluation enables clinicians to establish an accurate diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment strategy.
Read also:Find Bollywood More Streaming Guide News Movies
The ability to differentiate between normal and abnormal pupil dilation is essential for appropriate patient care. The evaluation of mydriasis is best carried out by a specialist in neuro.
The term "mydriasis" refers to the enlargement of the pupil beyond its normal size. It's essential to distinguish mydriasis from conditions that mimic it, such as eye injuries that may cause the pupil to appear dilated. Differentiating between the causes of mydriasis is critical for guiding management decisions.
When addressing mydriasis, it's important to consider various factors, including the patient's medical history, current medications, drug use, and any associated symptoms, to uncover the underlying reason for pupillary dilation. Also, note the pupil's reaction to light and near-vision, and this evaluation provides useful diagnostic information.
In cases of traumatic mydriasis, the specific mechanism of the injury and the resulting structural damage to the eye need to be thoroughly examined. Assessing the patient's accommodation, the ability to change focus for near and distant vision, is critical. Proper management and treatment of traumatic mydriasis also require a comprehensive approach that considers both the immediate and long-term visual consequences.
.jpg)