Is it possible that a seemingly innocuous medication can trigger a life-threatening condition? Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS), a rare but serious adverse reaction, underscores the complex and often unpredictable ways our bodies respond to certain drugs.
The clinical landscape of medicine is constantly evolving, driven by both groundbreaking discoveries and the ongoing quest to understand the intricacies of human health. Within this dynamic field, adverse drug reactions represent a significant area of concern, requiring constant vigilance and a deep understanding of potential risks. One such adverse reaction, Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS), serves as a potent example of the complexities involved. Though rare, its potential for severe consequences necessitates a comprehensive grasp of its underlying mechanisms, diagnostic criteria, and available treatment options.
The temporal progression of signs and symptoms is a critical element in understanding and managing NMS. The order in which symptoms appear can provide valuable clues regarding the diagnosis and the severity of the illness. Retrospective analyses offer compelling evidence, indicating that changes in mental status and other neurological signs frequently precede systemic manifestations in a substantial majority of NMS cases. This understanding of the symptom timeline is vital for early recognition and intervention.
Read also:Sdmoviespoint Is It Safe Features Risks Alternatives Guide
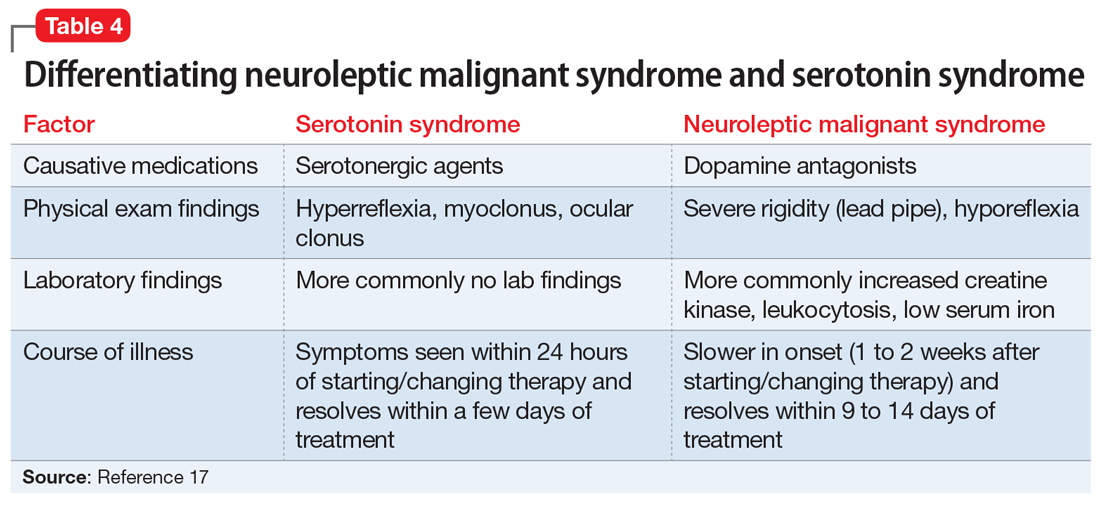
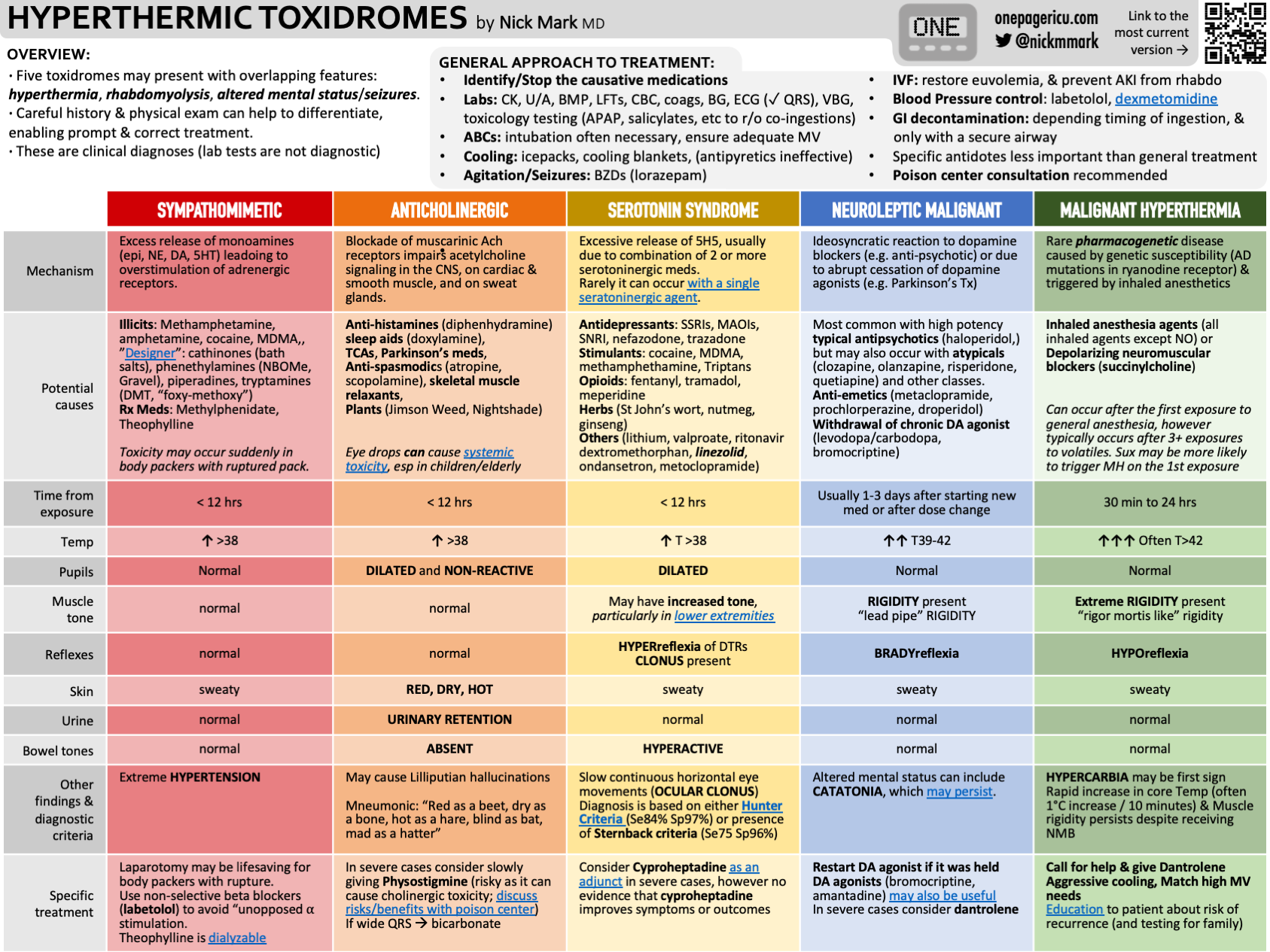
NMS doesn't have a single, definitive laboratory test to confirm it. However, it presents with a distinct clinical profile. This includes a constellation of symptoms that, when considered together, strongly suggest the diagnosis. This presentation usually includes alterations in mental status, such as confusion, agitation, or coma. It also involves muscle rigidity, where muscles become stiff and difficult to move. Hyperthermia, or a dangerously high body temperature, is a key indicator, and autonomic nervous system manifestations, such as rapid heart rate (tachycardia) and high blood pressure, are also common.
The roots of NMS trace back to the advent of neuroleptic drugs in the late 1950s. These medications, primarily used to treat psychotic disorders, were revolutionary at the time. However, the introduction of these powerful drugs also brought with it the potential for serious side effects, including the emergence of NMS. This syndrome was initially recognized as a distinct entity, a consequence of the very treatments designed to alleviate mental illness.
In its classic form, NMS is often recognizable. Yet, several factors complicate its management. The absence of specific diagnostic criteria, coupled with the rarity of its occurrence, has hindered research into its underlying mechanisms, clinical presentation, and treatment options. This means that healthcare professionals must rely on a keen understanding of the clinical picture and a high degree of suspicion to make a timely and accurate diagnosis. The rarity of the condition also limits the scope of large-scale clinical trials, making it challenging to evaluate the effectiveness of various treatment strategies.
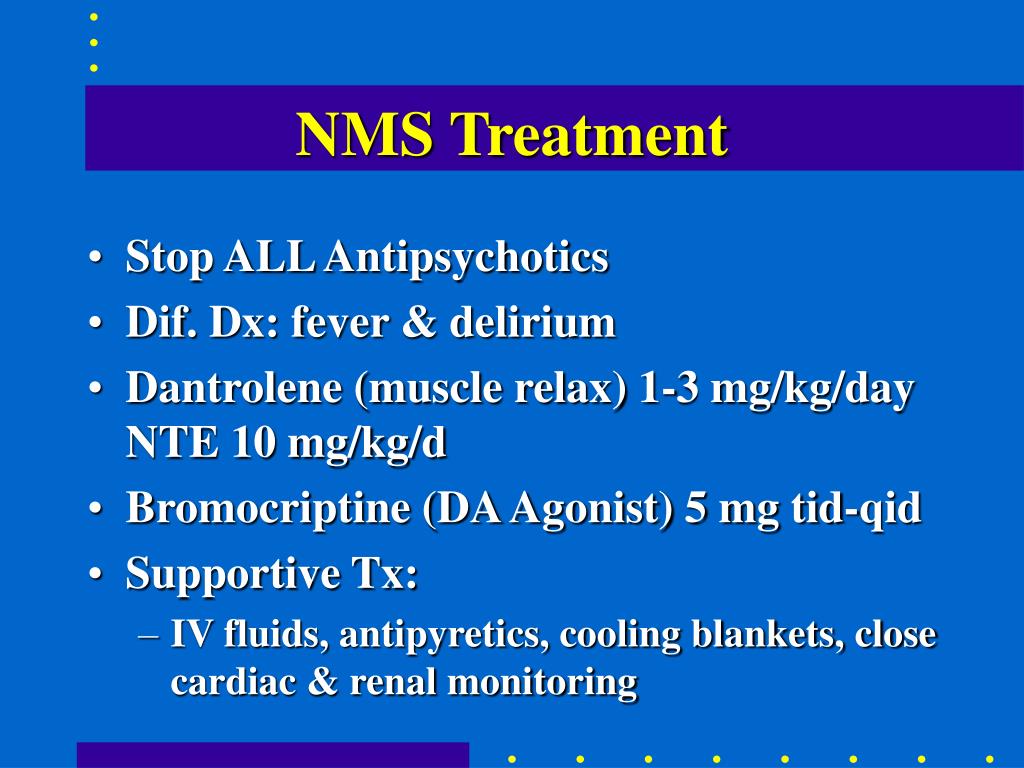
A critical element of NMS management involves medication review and adjustment. The relationship between escalating doses of certain medications, such as haloperidol, and temperature measurements warrants close scrutiny. When NMS is suspected, the offending agent is usually discontinued. This is often followed by the implementation of supportive measures and specific pharmacological interventions aimed at reversing the effects of the syndrome.
A typical treatment approach involves a combination of strategies. Medications such as dantrolene sodium and bromocriptine are often employed. Intravenous dantrolene, in particular, is frequently used to combat muscle rigidity and hyperthermia. Bromocriptine, a dopamine agonist, may also be used to address the underlying dopaminergic dysfunction. Furthermore, supportive care plays a crucial role, including cooling measures, such as cooled normal saline and cooling blankets, as well as aggressive hydration to maintain fluid balance and support organ function.
One of the key goals of research in this area is to find the best ways to treat NMS. This includes exploring different treatment strategies and evaluating their effectiveness. A study could focus on the efficacy of different treatments, specifically exploring the use of dantrolene and other therapeutic interventions. The findings from such research can shape clinical practice, ultimately improving patient outcomes and providing a foundation for future investigations.
Read also:Kannada Movies 2025 Latest Releases Streaming More
To build a comprehensive understanding of NMS, studies often involve collecting and analyzing data from various sources, including case reports. These reports provide valuable insights into individual patient experiences and treatment outcomes. For instance, a study could include a review of numerous case reports, with the aim of identifying patterns, evaluating treatment responses, and uncovering potential risk factors. This kind of detailed analysis is instrumental in shaping clinical guidelines and driving evidence-based practice.
The complexity of NMS and the need for further research are clear. The lack of a definitive diagnostic test, the variable presentation of symptoms, and the rarity of the condition present significant challenges. However, ongoing research, including case report analyses and clinical trials, is essential. It is necessary to improve diagnostic accuracy, refine treatment protocols, and ultimately save lives. Collaboration among healthcare professionals, researchers, and patients is crucial to advancing our understanding of NMS and improving the quality of care for those affected by this devastating syndrome.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Condition | Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) |
| Nature | Rare, but sometimes fatal, adverse reaction to neuroleptic medications. |
| Primary Symptoms | Fever and Rigidity |
| Characteristic Presentation | Changes in mental status, muscle rigidity, hyperthermia, autonomic nervous system manifestations (tachycardia, hypertension). |
| Typical Treatment Strategies | Discontinuation of causative neuroleptic, dantrolene sodium, bromocriptine, supportive care (cooling, hydration). |
| Diagnostic Challenges | Lack of a confirmatory laboratory test, rarity of the condition. |
| Historical Context | First described in the late 1950s with the introduction of neuroleptic drugs. |
| Research Focus | Understanding clinical presentation, pathophysiology, and treatment effectiveness. |
| Reference Website | UpToDate: Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome |